Use Lit Protocol with Irys to securely encrypt and manage your onchain data.
Using Lit with Irys empowers developers with the ability to create innovative applications by combining secure, encrypted data with the power of data storage and execution.
Lit is a decentralized key management network for signing and encryption. Users can encrypt data and set custom decryption rules, such as owning specific NFTs, maintaining an ERC20 token balance, or any other logic they define.
Once encrypted, data can be uploaded onchain, offering guaranteed retrieval for as long as needed — whether for days or permanently. Only users who meet the defined decryption rules can access the data, making it ideal for secure and private use cases.
This opens up new use cases for builders, such as:
- Gating access to content
- Storing and securing private DePIN data
- Securely archiving sensitive AI data
- Encrypted content for decentralized social apps
- Decentralized identity verification
- Creating private data marketplaces
- Creating exclusive NFTs
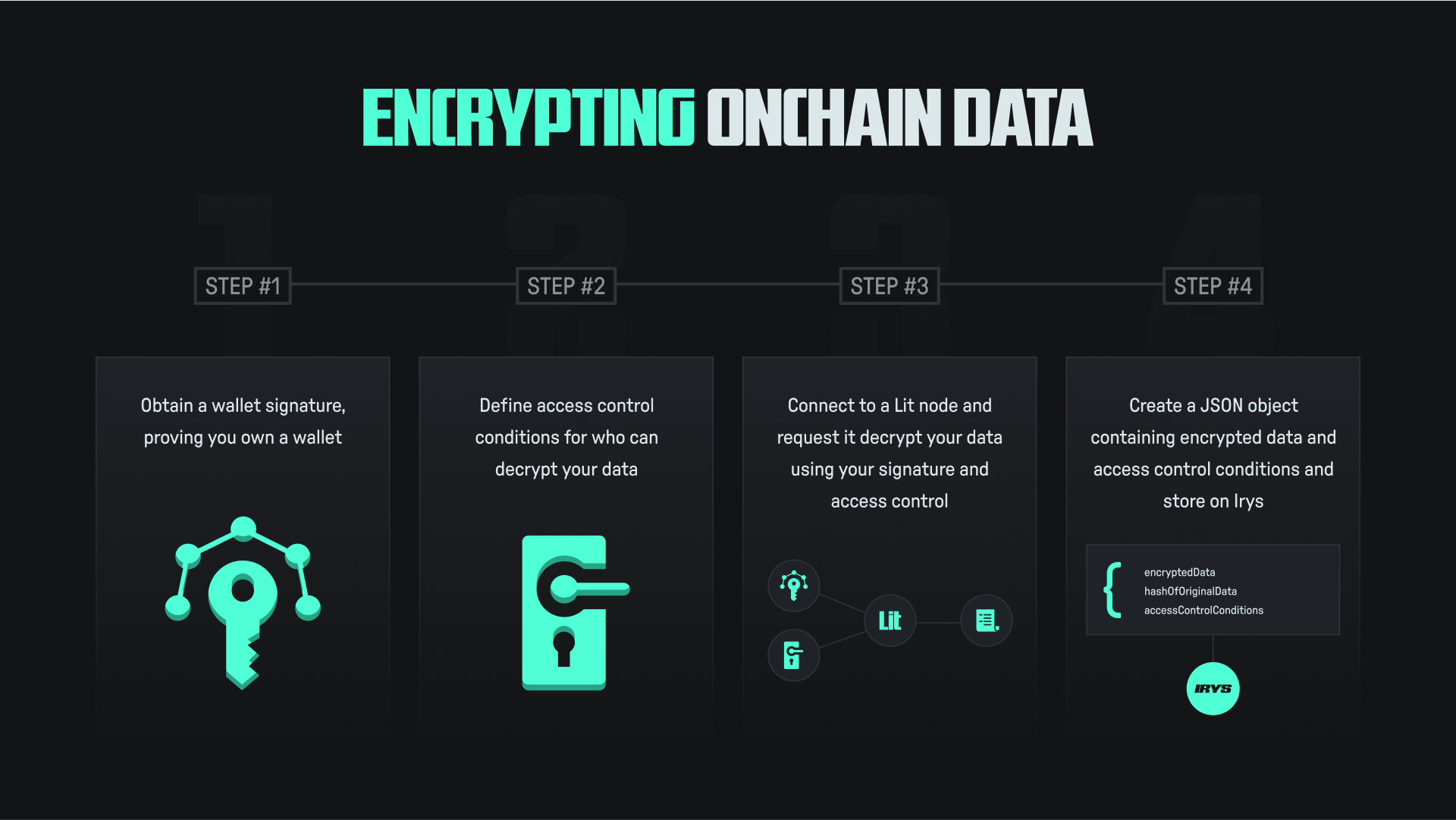
There are three steps to encrypting data:
- Obtain a wallet signature (AuthSig), which proves you own a wallet
- Define access control conditions for who can decrypt your data
- Connect to a Lit node and request that it encrypt your data

There are three steps to decrypting data:
- Obtain a wallet signature (AuthSig), which proves you own a wallet
- Retrieve data stored on Irys
- Connect to a Lit node and request that it decrypt your data
This guide covers integrating Lit with Irys, both with Node.js on the server and React/Next.js in the browser.
When working with Node.js, provide a private key when encrypting and decrypting data.
The full code for this example is available in the GitHub repository. Users who prefer learning by example can start there.
npm install \
@lit-protocol/lit-node-client-nodejs \
@lit-protocol/constants \
@irys/upload \
@irys/upload-ethereum \
ethers \
siwe \
dotenv
Connect to a Lit node on one of its active networks. Choose between Datil (mainnet), Datil-test (testnet), and Datil-dev (development). For this example, we'll use DatilDev as use is free and not rate-limited.
import * as LitJsSdk from "@lit-protocol/lit-node-client-nodejs";
import { LitNetwork } from "@lit-protocol/constants";
let litNodeClientInstance: LitJsSdk.LitNodeClientNodeJs | null = null;
async function getLitNodeClient(): Promise<LitJsSdk.LitNodeClientNodeJs> {
if (litNodeClientInstance) return litNodeClientInstance;
litNodeClientInstance = new LitJsSdk.LitNodeClientNodeJs({
alertWhenUnauthorized: false,
litNetwork: LitNetwork.DatilDev, // DatilDev network for free usage
debug: false,
});
await litNodeClientInstance.connect();
return litNodeClientInstance;
}
Access control rules determine who can decrypt your data. Set conditions based on criteria like ETH or ERC20 balance, NFT ownership, or custom logic.
// Allow users with ≥ 0 ETH:
function getAccessControlConditions(): object[] {
return [
{
contractAddress: "",
standardContractType: "",
chain: "ethereum",
method: "eth_getBalance",
parameters: [":userAddress", "latest"],
returnValueTest: {
comparator: ">=",
value: "000000000000000000", // 0 ETH in wei
},
},
];
}
For more advanced examples, see unified access control conditions.
Lit Protocol provides multiple methods to encrypt data, including strings, files, zip files.
encryptString():Encrypts a string.encryptToJson(): Encrypts a string or file and serializes the result to JSON.zipAndEncryptString(): Encrypts and compresses a string into a zip file. Useful for bundling multiple pieces of data.encryptFile()andzipAndEncryptFiles(): Encrypt a single file or multiple files.
We will use encryptString() to encrypt a simple string:
async function encryptData(dataToEncrypt: string): Promise<[string, string]> {
const authSig = await getAuthSig();
const accessControlConditions = getAccessControlConditions();
const litNodeClient = await getLitNodeClient();
const { ciphertext, dataToEncryptHash } = await LitJsSdk.encryptString(
{ accessControlConditions, dataToEncrypt },
litNodeClient
);
return [ciphertext, dataToEncryptHash];
}
The encryptString() function encrypts your data according to the specified access control conditions, and returns:
ciphertext: The encrypted string.dataToEncryptHash: The hash of the original string, ensuring data integrity.
When storing encrypted data on Irys, store it as a JSON object with three components:
ciphertext: The encrypted version of your data.dataToEncryptHash: A hash of the original data, which helps verify its integrity during decryption.accessControlConditions: The rules governing who can decrypt the data.
async function storeOnIrys(cipherText: string, dataToEncryptHash: string): Promise<string> {
const irysUploader = await getIrysUploader();
const dataToUpload = {
cipherText,
dataToEncryptHash,
accessControlConditions: getAccessControlConditions(),
};
try {
const tags = [{ name: "Content-Type", value: "application/json" }];
const receipt = await irysUploader.upload(JSON.stringify(dataToUpload), { tags });
return receipt?.id || "";
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error uploading data: ", error);
return "";
}
}
To retrieve your stored data, use the transaction ID returned at upload.
async function retrieveFromIrys(id: string): Promise<[string, string, object[]]> {
const gatewayAddress = "https://gateway.irys.xyz/";
const url = `${gatewayAddress}${id}`;
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Failed to retrieve data for ID: ${id}`);
const data = await response.json();
return [data.cipherText, data.dataToEncryptHash, data.accessControlConditions];
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error retrieving data: ", error);
return ["", "", []];
}
}
Use the decryptToString() function to decrypt the data. This requires the ciphertext, its hash, access control conditions, and session signatures.
async function decryptData(
ciphertext: string,
dataToEncryptHash: string,
accessControlConditions: object[]
): Promise<string> {
const litNodeClient = await getLitNodeClient();
const sessionSigs = await litNodeClient.getSessionSigs({
chain: "ethereum",
resourceAbilityRequests: [
{
resource: new LitAccessControlConditionResource("*"),
ability: LitAbility.AccessControlConditionDecryption,
},
],
authNeededCallback: async (params: any) => {
const toSign = await createSiweMessageWithRecaps({
uri: params.uri,
expiration: params.expiration,
resources: params.resourceAbilityRequests,
walletAddress: await (await new ethers.Wallet(process.env.PRIVATE_KEY!)).getAddress(),
nonce: await litNodeClient.getLatestBlockhash(),
litNodeClient,
});
return await generateAuthSig({
signer: new ethers.Wallet(process.env.PRIVATE_KEY!),
toSign,
});
},
});
const decryptedString = await LitJsSdk.decryptToString(
{
accessControlConditions,
chain: "ethereum",
ciphertext,
dataToEncryptHash,
sessionSigs,
},
litNodeClient
);
return decryptedString;
}
When working with Lit in the browser, the private key will be linked via the user's wallet extension.
The full code for this example, including a complete UI, is available in the GitHub repository. This guide focuses on the functions which handle interactions with Lit Protocol and Irys, but does not cover how to build and setup a UI.
npm install \
@lit-protocol/lit-node-client \
@irys/web-upload \
@irys/web-upload-ethereum \
@irys/web-upload-ethereum-ethers-v6 \
ethers
Connect to a Lit node on one of its active networks. Choose between Datil (mainnet), Datil-test (testnet), and Datil-dev (development). For this example, we'll use DatilDev as use is free and not rate-limited.
import * as LitJsSdk from "@lit-protocol/lit-node-client";
import { LitNodeClient } from "@lit-protocol/lit-node-client";
const litClient = new LitNodeClient({
litNetwork: "datil-dev",
});
Access control rules determine who can decrypt your data. Set conditions based on criteria like ETH or ERC20 balance, NFT ownership, or custom logic.
// Allow users with ≥ 0 ETH:
function getAccessControlConditions(): object[] {
return [
{
contractAddress: "",
standardContractType: "",
chain: "ethereum",
method: "eth_getBalance",
parameters: [":userAddress", "latest"],
returnValueTest: {
comparator: ">=",
value: "000000000000000000", // 0 ETH in wei
},
},
];
}
For more advanced examples, see unified access control conditions.
Lit Protocol provides multiple methods to encrypt data, including strings, files, zip files.
encryptString(): Encrypts a string.encryptToJson(): Encrypts a string or file and serializes the result to JSON.zipAndEncryptString(): Encrypts and compresses a string into a zip file. Useful for bundling multiple pieces of data.encryptFile()andzipAndEncryptFiles(): Encrypt a single file or multiple files.
We will use encryptString() to encrypt a string:
export const encryptString = async (text: string): Promise<{ ciphertext: string; dataToEncryptHash: string }> => {
await litClient.connect();
const accessControlConditions = getAccessControlConditions();
const { ciphertext, dataToEncryptHash } = await LitJsSdk.encryptString(
{
accessControlConditions,
dataToEncrypt: text,
},
litClient
);
console.log({ ciphertext, dataToEncryptHash });
return { ciphertext, dataToEncryptHash };
};
The encryptString() function encrypts your data according to the specified access control conditions, and returns:
ciphertext: The encrypted string.dataToEncryptHash: The hash of the original string, ensuring data integrity.
When storing encrypted data on Irys, store it as JSON objet with three components:
ciphertext: The encrypted version of your data.dataToEncryptHash: A hash of the original data, which helps verify its integrity during decryption.accessControlConditions: The rules governing who can decrypt the data.
export const uploadToIrys = async (cipherText: string, dataToEncryptHash: string): Promise<string> => {
const irysUploader = await getIrysUploader();
const dataToUpload = {
cipherText: cipherText,
dataToEncryptHash: dataToEncryptHash,
accessControlConditions: getAccessControlConditions(),
};
try {
const tags = [{ name: "Content-Type", value: "application/json" }];
const receipt = await irysUploader.upload(JSON.stringify(dataToUpload), { tags });
return receipt?.id ? `${gatewayAddress}${receipt.id}` : "";
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error uploading data: ", error);
throw error;
}
};
To retrieve your stored data, you can use the transaction ID returned during the upload.
export const downloadFromIrys = async (id: string): Promise<[string, string, object[]]> => {
const url = `${gatewayAddress}${id}`;
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Failed to retrieve data for ID: ${id}`);
const data = await response.json();
const ciphertext = data.cipherText;
const dataToEncryptHash = data.dataToEncryptHash;
return [ciphertext, dataToEncryptHash, data.accessControlConditions];
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error retrieving data: ", error);
return ["", "", []];
}
};
Use the decryptToString() function to decrypt the data. This requires the ciphertext, its hash, access control conditions, and session signatures.
export const decryptData = async (encryptedText: string, dataToEncryptHash: string): Promise<string> => {
await litClient.connect();
const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
const signer = await provider.getSigner();
const walletAddress = await signer.getAddress();
const latestBlockhash = await litClient.getLatestBlockhash();
const authNeededCallback = async (params: any) => {
if (!params.uri) throw new Error("uri is required");
if (!params.expiration) throw new Error("expiration is required");
if (!params.resourceAbilityRequests) throw new Error("resourceAbilityRequests is required");
const toSign = await createSiweMessageWithRecaps({
uri: params.uri,
expiration: params.expiration,
resources: params.resourceAbilityRequests,
walletAddress: walletAddress,
nonce: latestBlockhash,
litNodeClient: litClient,
});
const authSig = await generateAuthSig({
signer: signer,
toSign,
});
return authSig;
};
const litResource = new LitAccessControlConditionResource("*");
const sessionSigs = await litClient.getSessionSigs({
chain: "ethereum",
resourceAbilityRequests: [
{
resource: litResource,
ability: LitAbility.AccessControlConditionDecryption,
},
],
authNeededCallback,
});
const decryptedString = await LitJsSdk.decryptToString(
{
accessControlConditions: getAccessControlConditions(),
chain: "ethereum",
ciphertext: encryptedText,
dataToEncryptHash,
sessionSigs,
},
litClient
);
return decryptedString;
};
Any questions? Reach out to us in Discord.